Your download url is loading / ダウンロード URL を読み込んでいます

Your download url is loading / ダウンロード URL を読み込んでいます
Your download url is loading / ダウンロード URL を読み込んでいます
Whereas every cloud vendor could have a safe resolution for their very own cloud service and provide a wealthy set of safety instruments to its prospects, how can corporations make sure that they’re protected throughout all of the totally different boundaries of cloud implementations they make use of? That is particularly essential in the event that they don’t wish to implement a number of impartial safety mechanisms, or must cope with safety logs and information flows which can be incompatible?
Why is that this a problem? As a result of the typical firm has three-five totally different cases of cloud companies deployed of their enterprise– from public cloud to non-public cloud to hybrid cloud, to on-prem cloud — along with legacy information heart implementations. All of those have their very own means of defending the group from malware, information exfiltration and extra normal assaults. And with elevated emphasis on regulatory compliance necessities, the potential to handle all these disparate techniques is essential.
Though I estimate that about 50 to -60 p.c of corporations have carried out a SIEM (safety Info and occasion administration) resolution, which in principle aggregates risk intelligence data from quite a lot of sources (information heart, community routers, finish factors, cloud servers and so forth), it might or might not be absolutely built-in with every occasion of cloud in a multi-cloud setting. In reality, we’ve seen organizations that depend on the obtainable public cloud risk detection infrastructure by itself, fairly than even attempt to combine with an entire SIEM resolution.
That follow basically makes every cloud occasion a standalone risk administration system and requires the safety group to watch a number of data sources to see if they’re underneath assault. Additional, it’s fairly potential {that a} specific SIEM doesn’t assist the APIs for a specific cloud occasion that corporations are utilizing. And what ought to corporations that haven’t carried out a SIEM system do to handle their safety? At finest it is a messy scenario, and at worst, it may expose corporations to unneeded safety dangers current inside the gaps.
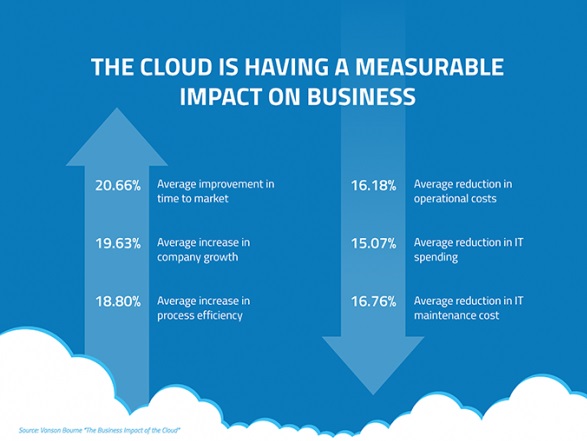
With so many company cloud service suppliers working with enterprises (e.g., AWS, Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure, Oracle, IBM, SAP, Alibaba, Baidu, Tencent and so forth.), it’s crucial that organizations discover a technique to share related security-oriented information from every and combination/consolidate that data right into a single system that may absolutely gather and analyze an entire set of all information, after which determine and pinpoint any safety breaches within the complete enterprise setting.
This sounds easy sufficient, however is not any simple process given the complexity of interactions and the number of information and community interactions going down, to not point out that many SIEMs are very tough to make use of for information evaluation functions and lots of corporations fall again to easy alerts that are essential however not ample.
So how does an enterprise extract information from a number of cloud environments and analyze the mandatory information from their SIEM (e.g., Splunk, McAfee, IBM, HP, RSA and others)?
One method to combating this complexity and siloed method to safety is the Open Cyber Safety Alliance. Its acknowledged aim (from its web site) is to convey “collectively distributors and finish customers in an open cybersecurity ecosystem the place merchandise can freely trade data, insights, analytics and orchestrated response. The OCA helps generally developed code and tooling and the usage of mutually agreed upon applied sciences, information requirements, and procedures.”
Whereas it is a generic open sourced safety information sharing group, it might have a number of longer-term ramifications not solely with stand alone techniques, however with cloud-based techniques as nicely. In the intervening time, numerous cloud distributors are taking their very own method whereas the open techniques work performs out over the subsequent 1-2 years or extra.
One instance of how a https://share.colinnex.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/08/multicloud setting for safety could also be carried out is the IBM Cloud Pak for Safety. IBM’s method is to pre-package an answer that has built-in integrations with the main cloud platforms and SIEM instruments (e.g., Splunk, AWS, Azure, Google Cloud, McAfee or others). It makes use of Purple Hat’s Open Shift platform. Open Shift permits interconnections to nearly any Linux setting and consists of practically all cloud-based techniques. However IBM’s method nonetheless requires connectors to be constructed to clouds and safety instruments, and in the event you want one not at the moment supported, IBM companies might want to construct it for you.
Microsoft additionally needs to be your main cross-cloud supplier of safety companies, however has a extra disjointed method with its myriad of safety merchandise. Not like IBM that’s making an attempt to merge all of its merchandise right into a single package deal, Microsoft has plenty of distinct merchandise like Azure Safety Middle, Microsoft Software Safety Companies, and Microsoft Cloud App Safety (A Cloud App Safety Dealer, or CASB). This raises the complexity of safety administration.
For its half, Google Cloud tends to have a lot better focus by itself safety than making an attempt to combine throughout all totally different cloud platforms. It has a wealthy set of instruments that cowl infrastructure safety, community safety, endpoint safety (primarily Chromebooks), information safety and Identification and Entry administration (IAM). It does have some cross platform functionality, but it surely must do extra.